
Sun safety made simple
Sun exposure is unavoidable. And with so much information out there, it can be hard to know the best way to protect your skin. Blue Lizard is here to make it easy, with just a few simple steps–and many great products–to help you and your family stay protected in the sun.
Two types of UV rays reach the earth’s surface: UVA and UVB rays. Exposure to UVB rays causes skin damage, and our skin reacts by producing melanin as a defense. When there is more UVB exposure than our skin’s melanin can handle, the skin’s DNA is damaged, and a sunburn appears.

UVA rays make up about 95% of the UV light that reaches the earth's surface. They can cause premature aging, wrinkles and dark spots, as well as skin cancer, including melanoma. UVA rays can pass through windows and clouds, making them dangerous even when it doesn't feel sunny outside.
UVB rays are responsible for every beach-goer's enemy: sunburn. Like UVA rays, UVB rays are another leading cause of skin cancer.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is very specific when it comes to sun safety–and for good reason. Children experience a lot more sun exposure than adults. In fact, researchers estimate that we receive up to 80% of our total lifetime sun exposure before we turn 18.
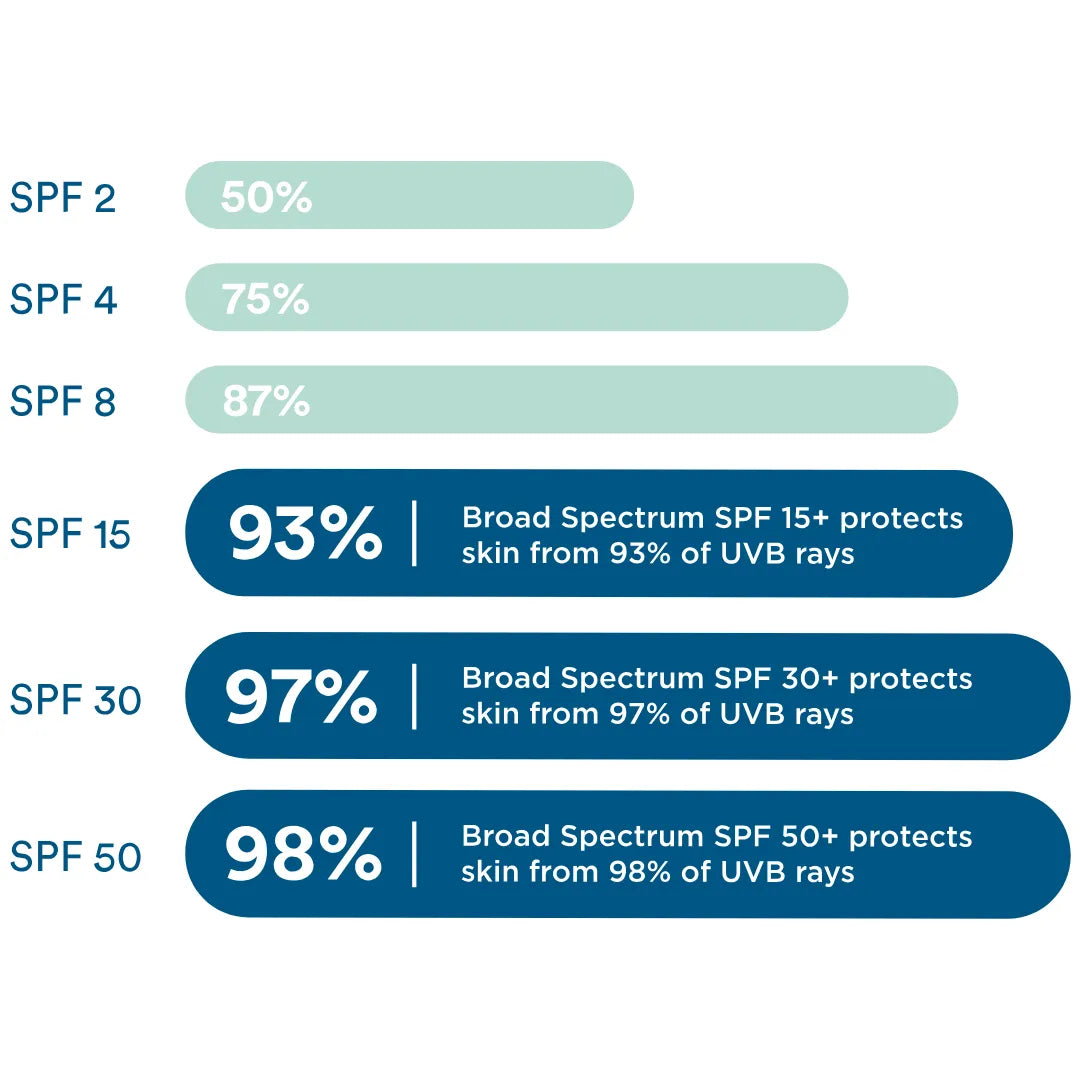
Sun protection factor (SPF) measures a sunscreen’s ability to help protect against UVB rays. Despite the common misconception, higher SPF does not always mean you are protected longer.
Every sunscreen should be reapplied at least every 2 hours. Most pediatricians and dermatologists recommend broad spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of at least 15 to 30+, which protects against up to 97% of UVB rays.

SPF stands for “Sun Protection Factor.” It measures a sunscreen’s ability to protect against UVB rays.
While some big sunscreen companies push the idea that higher SPF sunscreens keep you protected longer, the actual difference in protection is smaller than you may expect.
For adults: SPF 30 or higher, according to dermatologists
For children: SPF 15 or higher, according to pediatricians
Despite the common misconception, higher SPF does not always mean you are protected longer.

Blue Lizard partners with the Skin Cancer Foundation to encourage sun care education and improve skin health through protection, early detection, and treatment.
Learn more
Sunscreens aren’t a one-product-suits-all solution. If a child’s skin has turned red, swollen or developed eczema when wearing sunscreens, they may be having a reaction to some common ingredients.
For sensitive skin, dermatologists, allergists and pediatricians recommend using mineral sunscreens with Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide. Mineral sunscreens like Blue Lizard work by sitting on top of skin, making them less likely to irritate sensitive skin.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is very specific when it comes to sun safety–and for good reason. Children experience a lot more sun exposure than adults. In fact, researchers estimate that we receive up to 80% of our total lifetime sun exposure before we turn 18.
Kids need Vitamin D from a variety of sources to help grow healthy and strong. While our bodies naturally produce Vitamin D from sunlight, too much sun exposure can negatively affect our health. Even one blistering sunburn as a child can more than double your risk for melanoma.